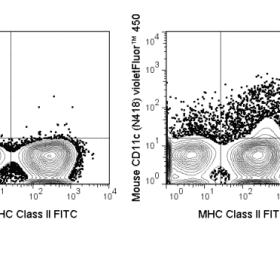
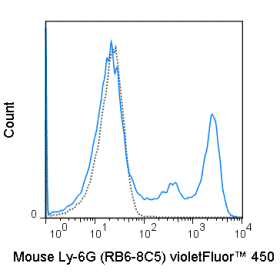
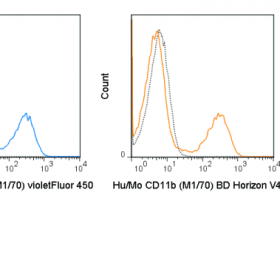
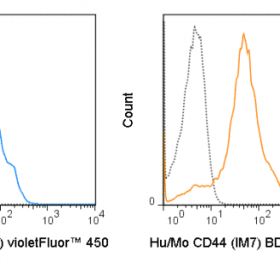
The CD28.2 antibody reacts with human CD28, a 44 kDa type I surface glycoprotein which acts as a co-stimulatory receptor in support of the T cell receptor (TCR). CD28 exists as a homodimer with specificity for two known ligands, known as B7-1 (CD80) and B7-2 (CD86), which are expressed on activated B cells and antigen-presenting cells. These ligands trigger CD28 signaling in concert with TCR activation to drive T cell proliferation, induce high-level expression of IL-2, impart resistance to apoptosis, and enhance T cell cytotoxicity. The interaction / co-stimulatory signaling between ≥ ≥ ≥ the B7 ligands and CD28 provides crucial communication between ≥ ≥ ≥ T cells and B cells or APCs to coordinate the adaptive immune response. Other members of the CD28 family of receptors include CTLA-4 (CD152), PD-1 (CD279), ICOS and BTLA.
The CD28.2 antibody may be used as a phenotypic marker for human CD28, expressed on all CD4+ T cells and CD8+ T cells, and is widely used as a reagent for activation of the CD28 receptor in vitro and in vivo (use format suitable for functional assays). This antibody is also reported to be cross-reactive with several non-human species, including Baboon, Chimpanzee, Cynomolgus, and Rhesus.
Product Details
| Name | PE-Cyanine7 Anti-Human CD28 (CD28.2) |
|---|---|
| Cat. No. | 60-0289 |
| Alternative Names | T44, Tp44 |
| Gene ID | 940 |
| Clone | CD28.2 |
| Isotype | Mouse IgG1, kappa |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Cross Reactivity | Baboon, Chimpanzee, Cynomolgus, Rhesus |
| Format | PE-Cyanine7 |
| Application | Flow Cytometry |
| Citations* | Griffin GK, Newton G, Tarrio ML, Bu D-X, Maganto-Garcia E, Azcutia V, Alcaide P, Grabie N, Luscinskas FW, Croce KJ, and Lichtman AH. 2012. J. Immunol. 188: 6287-6299. (in vitro activation)
Cocchi F, DeVico AL, Lu W, Popovic M, Latiinovic O, Sajadi MM, Redfield RR, Lafferty MK, Galli M, Garzino-Demo A, and Gallo RC. 2012. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 109: 5411-5416. (in vitro activation) Okoye AA, Rohankhedkar M, Abana C, Pattenn A, Reyes M, Pexton C, Lum R, Sylwester A, Planer SL, Legasse A, Park BS, Piatak M, Lifson JD, Axthelm MK and Picker LJ. 2012. J. Exp. Med. 209: 641-651. (Flow cytometry) Vanderford TH, Slichter C, Rogers KA, Lawson BO, Obaede R, Else J, Villinger F, Bosinger SE, and Silvestri G. 2012. Blood. 119: 5750-5757. (Flow cytometry – Sooty Mangabey) Ansari AA, Reimann KA, Mayne AE, Takahashi Y, Stephenson ST, Wang R, Wang X, Li J, Price AA, Little DM, Zaidi M, Lyles R, and Villinger F. 2011. J. Immunol. 186: 1044-1059. (Flow cytometry – Rhesus macaque Soto PC, Stein LL, Hurtado-Ziola N, Hedrick SA, and Varki A. 2010. J. Immunol. 184: 4185-4195. (in vitro activation – Chimpanzee) Di Carlo E, D’Antuono T, Pompa P, Giuliani R, Rosini S, Stuppia L, Musiani P, and Sorrentino C. 2009. Clin. Cancer Res. 15: 2979-2987. (Immunohistochemistry – frozen tissue) Berg M and Zavazava N. 2008. J. Leukoc. Biol. 83: 852-863. (Immunoprecipitation) Fos C, Salles A, Lang V, Carrette F, Audebert S, Pastor S, Ghiotto M, Olive D, Bismuth G, and Nunes JA. 2008. J. Immunol. 181: 1969-1977. (Immunoprecipation, Flow cytometry) |
Application Key:FC = Flow Cytometry; FA = Functional Assays; ELISA = Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay; ICC = Immunocytochemistry; IF = Immunofluorescence Microscopy; IHC = Immunohistochemistry; IHC-F = Immunohistochemistry, Frozen Tissue; IHC-P = Immunohistochemistry, Paraffin-Embedded Tissue; IP = Immunoprecipitation; WB = Western Blot; EM = Electron Microscopy
*Tonbo Biosciences tests all antibodies by flow cytometry. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Tonbo Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult the Materials and Methods section for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.