- Your cart is empty
- Continue Shopping
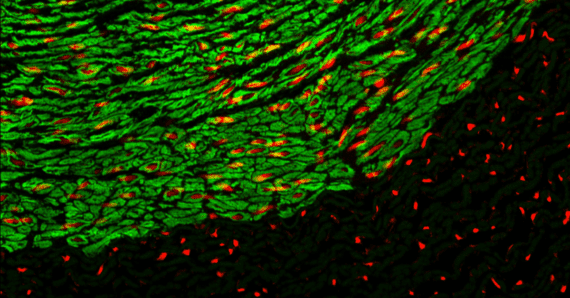
How are Mesenchymal Stem Cells harvested for research and potential therapies?
Uncover How Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) are Harvested for research and potential therapies. Explore various sources like bone marrow, umbilical cord, and adipose tissue. Learn about their applications and the importance of safety evaluation.