- Your cart is empty
- Continue Shopping
Researchers’ Guide to Cytokines: Detection and Analysis with ELISA Kits
Researchers’ Guide to Cytokines: Detection and Analysis with ELISA Kits
- Atlantis Bioscience
- Blog
- Reading Time: 4 minutes
Table of Contents
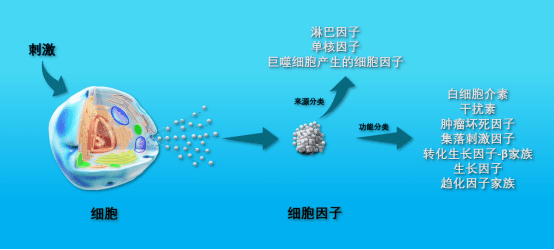
Cytokines (CKs) are small protein messengers playing a critical role in regulating various biological processes. Secreted by immune cells (monocytes, macrophages, T/B/NK cells) and non-immune cells (endothelial, epidermal, fibroblasts), these versatile molecules orchestrate communication between cells. Cytokines bind to specific receptors on target cells, triggering signal transduction pathways that exert diverse effects. Their actions can be categorized as autocrine (acting on the same cell that produced them), paracrine (affecting nearby cells), or endocrine (acting on distant cells).
Key Functions of Cytokines:
- Regulating Immunity: Cytokines orchestrate both innate and adaptive immune responses, helping the body fight off infections.
- Tissue Repair: Signaling pathways initiated by cytokines promote tissue repair and regeneration.
- Inflammation Modulation: Cytokines play a key role in initiating and regulating inflammatory responses.
- Stem Cell Regulation: They influence the behavior of pluripotent stem cells (APSCs).
- Cell Growth and Blood Cell Production: Cytokines are essential for regulating cell growth and blood cell production.
By understanding the diverse functions of cytokines, researchers can gain valuable insights into various physiological and pathological processes
Cytokine production and classification
Cytokines can be categorized based on their origin and function. Let’s break it down:
By Source:
- Lymphokines: Produced by lymphocytes (B, T, and NK cells). Examples include IL-2, IFN-γ, and GM-CSF.
- Monokines: Secreted by monocytes and macrophages. Examples include IL-1, TNF-α, and G-CSF.
- Other Cellular Cytokines: Produced by various cells like endothelial cells, stromal cells, and those in the bone marrow and thymus. Examples include IL-7 and IFN-β.
By Functions:
- Interleukins (ILs): These versatile messengers, produced by various cells, regulate immune responses, cell interactions, blood cell production, and inflammation.
- Interferons (IFNs): Based on structure and origin, IFNs can be IFN-α (leukocytes), IFN-β (fibroblasts), or IFN-γ (activated T cells). They play a crucial role in antiviral defense.
- Tumor Necrosis Factors (TNFs): TNF-α, produced by monocytes and macrophages or activated T cells, can induce tumor cell death. TNF-β exists in two forms.
- Colony Stimulating Factors (CSFs): These factors not only stimulate the development of blood cell precursors but also enhance the function of mature blood cells. Examples include G-CSF (granulocyte), M-CSF (macrophage), and GM-CSF (both granulocyte and macrophage).
- Transforming Growth Factor-β (TGF-β) Family: These factors include TGF-β1, TGF-β2, etc., and influence cell growth, differentiation, and immune regulation.
- Growth Factors (GFs): This diverse group includes epidermal growth factor (EGF), fibroblast growth factor (FGF), nerve growth factor (NGF), and others, involved in cell proliferation and development.
- Chemokine Family: Chemokines, categorized into subfamilies based on structure, are responsible for directing the movement of immune cells.
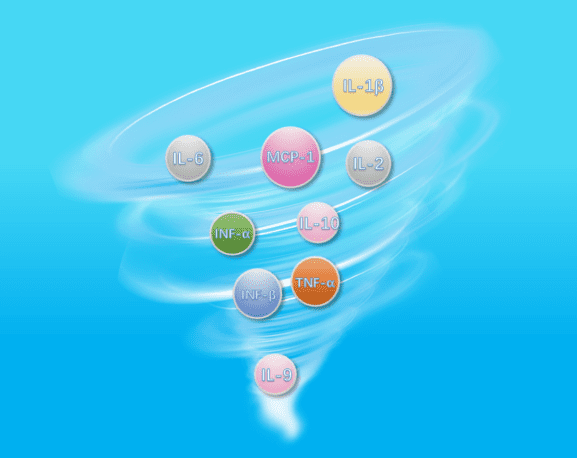
The Cytokine Storm: When Communication Turns Destructive
When the body encounters a severe challenge like a microbial infection, it triggers a rapid and massive release of various cytokines, including interleukins and chemokines. This phenomenon is called a cytokine storm.
Cytokines normally guide immune cells to fight infection and activate them. However, in a cytokine storm, the feedback loop goes haywire. Too many activated immune cells become concentrated, potentially due to an overreaction to a highly pathogenic threat. This excessive immune response can damage healthy tissues and organs. For example, in the lungs, it can lead to fluid buildup, hindering breathing and potentially causing death.
Understanding cytokine classification helps researchers decipher their roles in both healthy immune function and pathological conditions like cytokine storms.

Cytokines: Messengers of Inflammation and Immunity
Cytokines play a critical role as signaling molecules in the body’s immune response and inflammatory processes. Their levels fluctuate dynamically during disease progression, making them highly sensitive indicators of inflammation. By monitoring cytokine changes, healthcare professionals can potentially:
- Predict Disease Severity: Early detection of rising cytokine levels might signal a worsening disease course, allowing for timely intervention.
- Optimize Treatment Strategies: Understanding cytokine profiles can guide treatment decisions, potentially improving clinical outcomes and reducing the risk of complications.
Beyond clinical applications, cytokine detection serves as a valuable tool in biomedical research. Analyzing cytokine content and distribution helps researchers gain deeper insights into various disease processes.
ELISA: The Gold Standard for Cytokine Detection
How do you detect cytokine in the lab? Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) has emerged as a powerful technology for detecting various biomolecules, including cytokines. It elegantly combines the specificity of antigen-antibody interactions with the efficiency of enzymatic reactions.
How to choose an ELISA Kit for cytokine detection
Picking the right ELISA kit offers numerous advantages for cytokine detection. Here’s what you should look for:
- High Specificity: Precisely targets the cytokine of interest, minimizing interference from other molecules.
- Enhanced Sensitivity: Detects even minute quantities of cytokines, crucial for early disease detection.
- Simplified Operation: Streamlined procedures make ELISA user-friendly for researchers and clinical labs.
- Efficient Detection: Provides accurate and reliable cytokine measurements.
At Atlantis Bioscience, we recognize the importance of reliable tools for cytokine detection. We are proud to offer high-quality ELISA kits from ELK Biotech as a trusted source for global researchers and clinicians. ELK Biotech’s ELISA kits are renowned for their:
- Efficiency: Streamlined protocols for rapid and cost-effective analysis.
- High Specificity: Antibodies specifically target your cytokine of interest for accurate results.
- Ease of Use: User-friendly protocols ensure successful experimentation for researchers of all experience levels.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Competitive pricing makes cytokine detection accessible for a wider range of research projects.
Hence, they have a wide range of loyal users globally. Explore our selection of ELK Biotech ELISA kits today and unlock the power of cytokine detection in your research!
Types of ELISA Kits for Cytokine detection that we’ve curated for researchers and scientist in Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam, Indonesia and Korea:
(As these products are not listed on our website, you can fill up our contact us form or email us at [email protected])
References
CONTACT

QUESTIONS IN YOUR MIND?
Connect With Our Technical Specialist.

KNOW WHAT YOU WANT?
Request For A Quotaiton
OTHER BLOGS YOU MIGHT LIKE
HOW CAN WE HELP YOU? Our specialists are to help you find the best product for your application. We will be happy to help you find the right product for the job.

TALK TO A SPECIALIST
Contact our Customer Care, Sales & Scientific Assistance

EMAIL US
Consult and asked questions about our products & services

DOCUMENTATION
Documentation of Technical & Safety Data Sheet, Guides and more..
