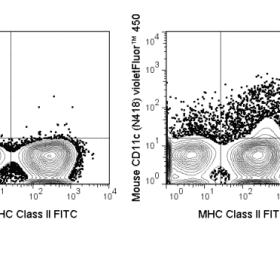
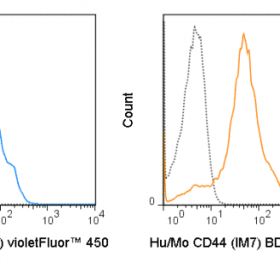
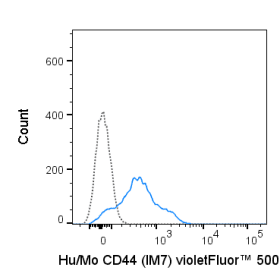
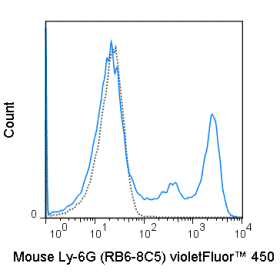
The RPA-T4 antibody reacts with human CD4, a 59 kDa protein which acts as a co-receptor for the T cell receptor (TCR) in its interaction with MHC Class II molecules on antigen-presenting cells. The extracellular domain of CD4 binds to the beta-2 domain of MHC Class II, while its cytoplasmic tail provides a binding site for the tyrosine kinase lck, facilitating the signaling cascade that initiates T cell activation. CD4, and co-receptors CCR5 and CXCR4, may also be utilized by HIV-1 to enter T cells. Human CD4 is typically expressed on thymocytes, some mature T cell populations such as Th17 and T regulatory (Treg) cells, as well as on dendritic cells.
The RPA-T4 antibody is widely used as a phenotypic marker for human CD4 expression, and is cross-reactive with Chimpanzee CD4. This antibody recognizes a different epitope, and thus does not block binding of, the alternative Anti-Human CD4 antibody clone OKT4 (Reinherz EL, et al. 1979. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 76:4061-4065).
Product Details
| Name | violetFluor™ 450 Anti-Human CD4 (RPA-T4) |
|---|---|
| Cat. No. | 75-0049 |
| Alternative Names | Leu-3, T4 |
| Gene ID | 920 |
| Clone | RPA-T4 |
| Isotype | Mouse IgG1, kappa |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Cross Reactivity | Chimpanzee |
| Format | violetFluor™ 450 |
| Application | Flow Cytometry |
| Citations* | Toma J, Weinheimer SP, Stawiski E, Whitcomb JM, Lewis ST, Petropoulos CJ, and Huang W. 2011. J. Virol. 85: 3872-3880. (Blocking: HIV-1 interaction)
Porter KA, Kelley LN, Nekorchuk MD, Jones JH, Hahn AB, de Noronha CMC, Harton JA, and Duus KM. 2010. J. Immunol. 185:6480-6488. (Blocking: HIV-1 interaction) Hsieh S-C, Tsai W-Y, and Wang W-K. 2010. J. Virol. 84(9) : 4782-4797. (Immunoprecipitation – transfected cells)Chen X, Wang X, Besra GS, and Gumperz JE. 2007. J. Leukoc. Biol. 82:1455-1465. (in vitro activation) Thedrez A, de Lalla C, Allain S, Zaccagnino L, et al. 2007. Blood. 110:251-258 (in vitro blocking) Mack CL, Tucker RM, Sokol RJ, Darrer FM, Kotzin BL, Whitington PF and Miller SD. 2004. Pediatr. Res. 56(1) :79-87. (Immunohistochemistry – frozen tissue)Deng MC, Bell S, Huie P, Pinto F, Hunt SA, Stinson EB, Sibley R, Hall BM, and Valantine HA. 1995. Circulation. 91: 1647-1654. (Immunohistochemistry – OCT embedded frozen tissue) |
Application Key:FC = Flow Cytometry; FA = Functional Assays; ELISA = Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay; ICC = Immunocytochemistry; IF = Immunofluorescence Microscopy; IHC = Immunohistochemistry; IHC-F = Immunohistochemistry, Frozen Tissue; IHC-P = Immunohistochemistry, Paraffin-Embedded Tissue; IP = Immunoprecipitation; WB = Western Blot; EM = Electron Microscopy
*Tonbo Biosciences tests all antibodies by flow cytometry. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Tonbo Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult the Materials and Methods section for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.